Ketamine and Neuroplasticity: A Window into Brain Healing
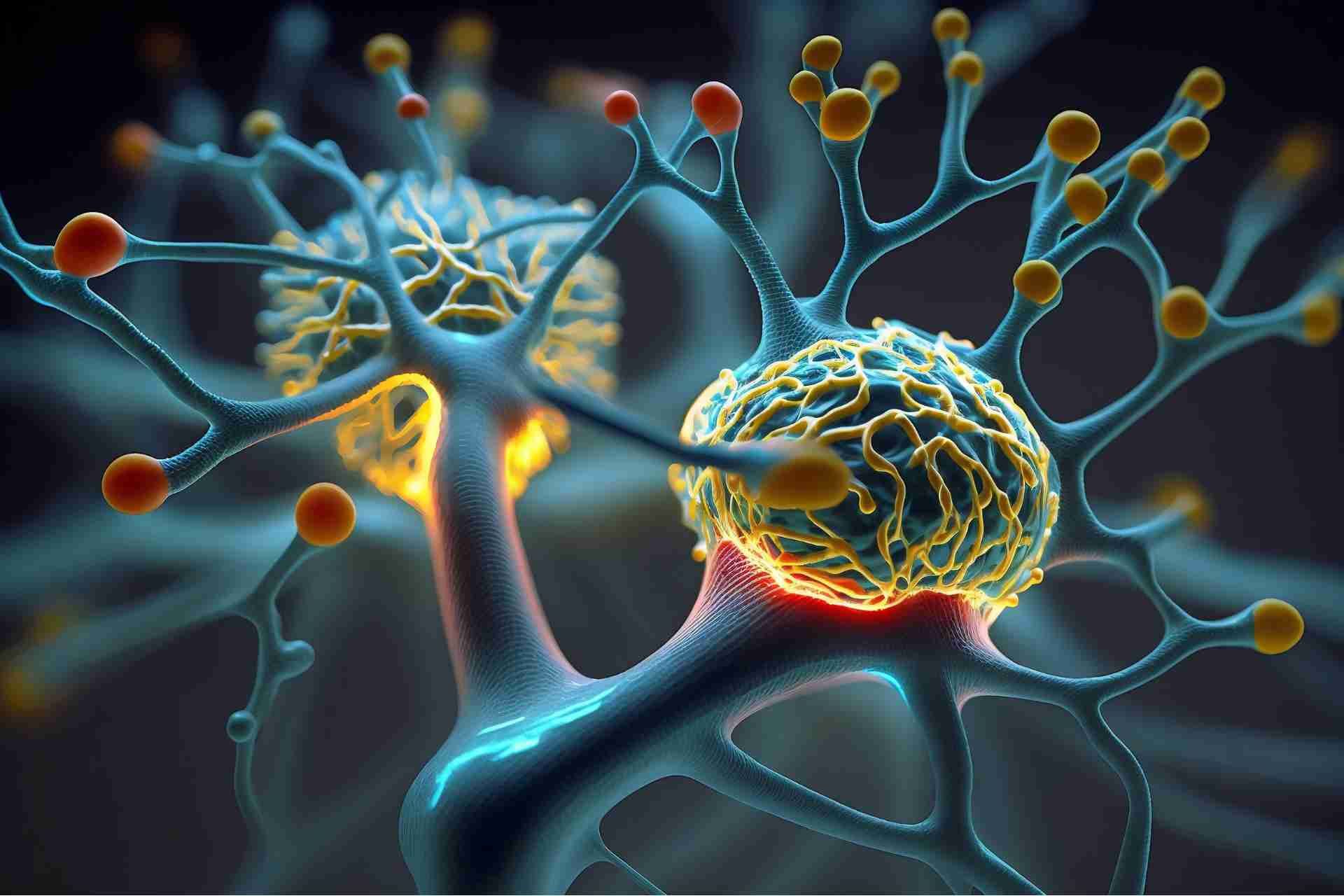
Ketamine is changing the way we think about mental health treatment. By promoting neuroplasticity, it helps the brain form new connections, which can be crucial for healing. This ability to reshape thought patterns offers hope for those struggling with conditions like depression and PTSD. But how exactly does ketamine achieve this? Understanding the science behind its effects is essential to grasp its potential completely.
The Science Behind Ketamine and Its Effects on the Brain
When you explore the science behind ketamine, you'll find that it acts primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist, which means it blocks certain neurotransmitter signals in the brain.
This action leads to a rapid increase in glutamate, a crucial neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory. By disrupting typical pathways, ketamine creates a unique environment that facilitates synaptic plasticity.
This allows for the formation of new connections between neurons, which is essential for healing from depression and other mental health disorders. Additionally, ketamine's effects can be felt within hours, unlike traditional antidepressants that often take weeks.
Its ability to promote neural growth and adaptability is a promising avenue in mental health treatment, paving the way for innovative therapeutic approaches.
Understanding Neuroplasticity and Its Importance in Mental Health
Neuroplasticity, the brain's remarkable ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections, plays a crucial role in mental health. It allows you to adapt to new experiences, learn from challenges, and recover from trauma.
When you face stress or adversity, your brain can reshape itself, helping you develop healthier thought patterns and coping mechanisms. This adaptability is essential for overcoming mental health issues like depression and anxiety.
By engaging in activities that promote neuroplasticity—such as learning new skills or practicing mindfulness—you can enhance your brain's resilience. Understanding this process empowers you to take an active role in your mental well-being.
Acknowledging neuroplasticity's importance paves the way for personal growth and healing.
How Ketamine Promotes Synapse Formation
Ketamine has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment for mental health disorders, primarily due to its ability to promote synapse formation in the brain.
By enhancing synaptic connections, ketamine helps restore neural pathways, leading to improved communication between brain cells. This process occurs quickly, often within hours of administration, which sets ketamine apart from traditional antidepressants.
You might experience increased synaptic density, allowing for more robust neural networks. Additionally, ketamine stimulates the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein essential for neuron growth and survival.
This surge in BDNF further supports synapse formation, enabling your brain to adapt and heal. Overall, ketamine's unique mechanism offers a promising avenue for fostering neuroplasticity and enhancing cognitive function.
Clinical Applications: Ketamine in Treating Mental Health Disorders
As mental health disorders become increasingly prevalent, innovative treatments like ketamine have gained attention for their rapid and effective relief of symptoms. Many people struggling with conditions like depression, anxiety, and PTSD have found that traditional therapies often fall short.
Ketamine, however, works differently by targeting the brain's glutamate system, promoting neuroplasticity and fostering new connections. This unique mechanism can lead to a swift improvement in mood and cognitive function, often within hours.
Administered through various methods, including intravenous infusions and nasal sprays, ketamine's flexibility makes it accessible for many patients.
As you explore treatment options, consider discussing ketamine with your healthcare provider to see if it might be the right fit for your mental health journey.
Future Directions in Ketamine Research and Neuroplasticity
While current research has shown promising results in using ketamine to enhance neuroplasticity, the future holds even greater potential for understanding its mechanisms and applications.
You might see studies focusing on optimal dosing strategies, aiming to maximize benefits while minimizing side effects. Researchers could explore ketamine's impact on various brain regions, revealing specific pathways involved in neuroplasticity.
Additionally, combining ketamine with other therapeutic modalities, like psychotherapy or exercise, may enhance outcomes. As you follow these developments, keep an eye on how emerging techniques, such as neuroimaging, help visualize changes in the brain.
Ultimately, these advancements could lead to more personalized treatment approaches, transforming how we address mental health and neurological disorders through neuroplasticity.
Conclusion
In summary, ketamine offers a unique approach to mental health treatment by enhancing neuroplasticity and fostering new neural connections. This breakthrough could change the way we address issues like depression, anxiety, and PTSD. As research continues to unfold, the potential for ketamine to reshape our understanding of brain healing is promising. Embracing this innovative therapy might just be the key to unlocking healthier thought patterns and improved mental well-being for many individuals.